Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
Introduction The first use of the term autophagy by
2024-09-18
Introduction The first use of the term “autophagy” by a French physiologist, M. Anselmier, in a short article describing the effects of fasting in mice published in 1859, took place almost a century before Christian De Duve described it from a mechanistic point of view in a symposium on lysosomes i
-
br Disclaimer Statement br Acknowledgments br Introduction
2024-09-18
Disclaimer Statement Acknowledgments Introduction Metabolic changes are a common feature of cancerous tissues. Mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes cause alterations to multiple intracellular signaling pathways that rewire tumor cell metabolism and re-engineer it to allow enhan
-
We also show that in
2024-09-18
We also show that in both ATM proficient and deficient/mutant cholecalciferol vitamin d3 the activation of ATR signaling is DSB complexity-dependent (Figs. 1, 4A, C and E, 6A and B). Wang et al. have also reported that the effects of ATR and CHK1 on radiosensitivity are independent of the NHEJ repa
-
Despite these conflicting data about COX ER correlations a
2024-09-14
Despite these conflicting data about COX-2/ER correlations, a large body of evidence supports that elevated COX-2 expression in breast cancer is a constant feature of high stage disease and a predictor of worse outcome. Upregulation of COX-2 protein has been identified in approximately 40% of cases
-
The therapeutic potential of ML induced MET against cells
2024-09-14
The therapeutic potential of ML327-induced MET against 87 59 synthesis of mesenchymal origin has not been explored. In the present study, we hypothesized that induction of MET using ML327 would block the growth of ES cells and sensitize to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Herein, we report that ML327 indu
-
Limitations of this study include the use of HL cardiomyocyt
2024-09-14
Limitations of this study include the use of HL-1 cardiomyocytes, which show different characteristics than primary cardiomyocytes [56]. Furthermore, sustained TAC in Ampkα1-deficient mice did not favorably influence cardiac function [33]. It must be kept in mind that global Ampkα1-deficiency may af
-
In our study S aureus activated the TLR signaling
2024-09-14
In our study, S. aureus activated the TLR signaling pathways of BMECs, thus inducing profibrogenic growth factor expression via NF-κB and AP-1. Since fibrosis is an important pathogenic process in both bovine and human mastitis, further studies on the molecular mechanisms of S. aureus infection are
-
br Results br Discussion Control of chronic inflammation is
2024-09-14
Results Discussion Control of chronic inflammation is important in several inflammatory conditions like asthma, rheumatoid arthritis and fibrosis in lung diseases. The regulatory pathways that control chronic inflammation are complex and multi-factorial. Over expression of inflammatory mediato
-
br Conflict of interest statement br Introduction Currently
2024-09-14
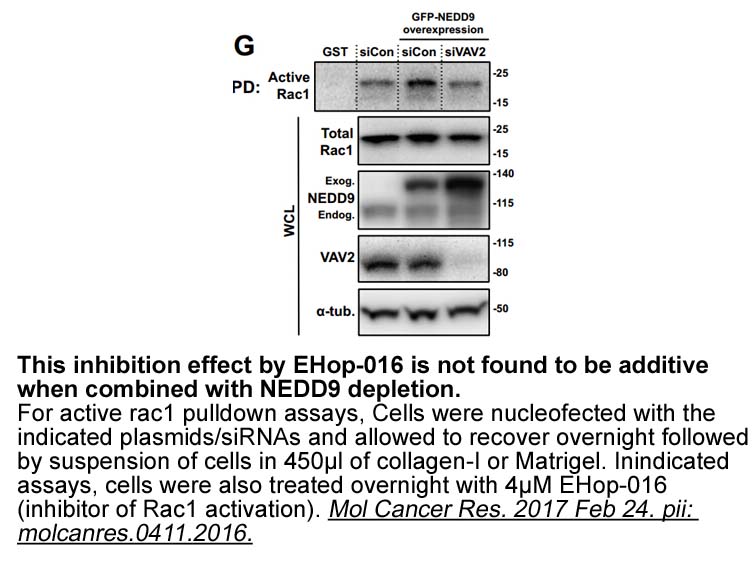
Conflict of interest statement Introduction Currently, adenocarcinoma is the most common histological subtype of lung cancer. Activating mutations and translocations with a potential for targeted therapy are reported predominantly in non-smokers. ALK rearrangement is found in less than 5% of u
-
HsALDH enzyme has been purified for
2024-09-14
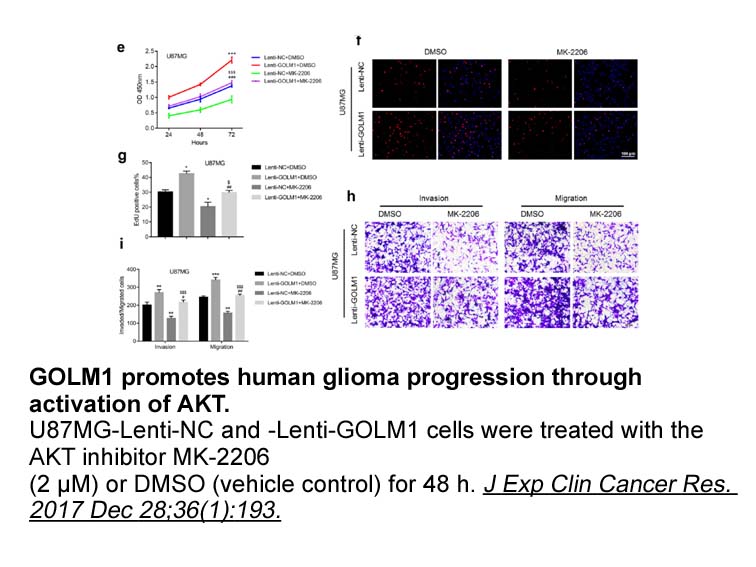
HsALDH enzyme has been purified for the first time in our laboratory from human saliva and has been kinetically characterized using different aromatic substrates [35]. Also, the effect of some common substances frequently encountered by the enzyme in the oral cavity (such as ethanol, hydrogen peroxi
-
In the vasculature it is known that
2024-09-14
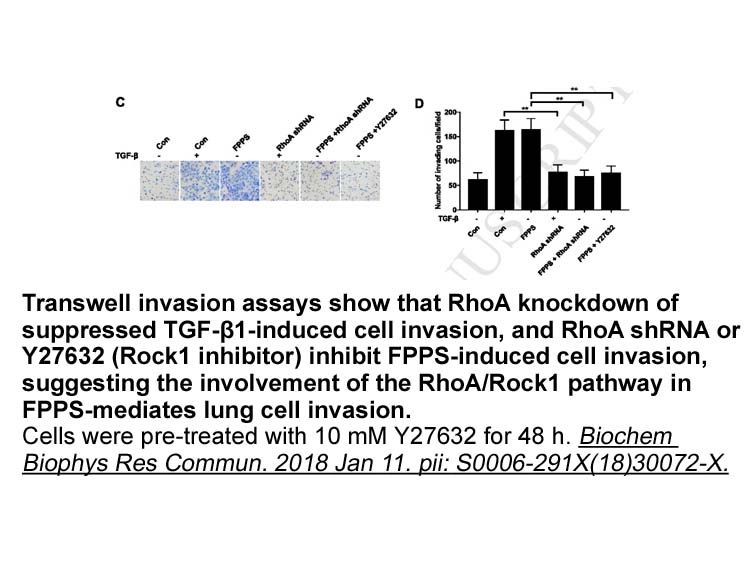
In the vasculature, it is known that A2A and A2B adenosine receptors are stimulatory for adenylyl-cyclase, leading to cyclic-AMP (cAMP) production and vasodilation, while the A1 and A3 adenosine receptors are linked to the inhibitory Gi, suppressing adenylyl-cyclase and favoring contraction. However
-
The myasthenia scale of Millichap
2024-09-14
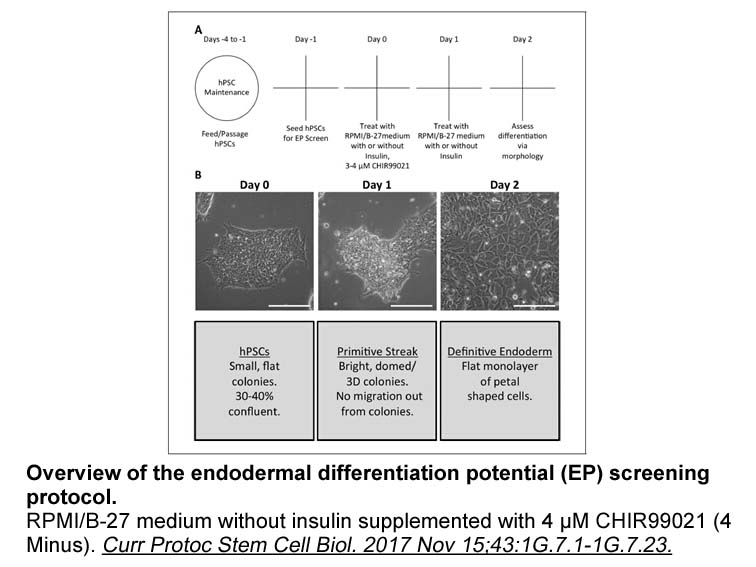
The myasthenia scale of Millichap and Dodge was used in our study for ease of comparison of our retrospective data with previous paediatric studies. Our results, with 30% achieving complete remission and 95% achieving at least some degree of clinical improvement following thymectomy, are comparable
-
br Dihydrotestosterone in adult fish and
2024-09-13
Dihydrotestosterone in adult fish and frogs New perspectives and next directions Similar to other androgens, DHT can modulate reproductive endpoints in both fish and amphibians. However, predicting the effects of DHT can be challenging, as reproductive homeostasis is dependent upon the balance
-
The first natural product described as LO
2024-09-13

The first natural product described as 5-LO inhibitor was the polyphenol nordihydroguaiaretic alk5 from the Mexican dessert plant Larrea divaricata in 1981 (Bokoch and Reed, 1981), short after the initial identification of 5-LO in 1979 (Borgeat and Samuelsson, 1979). Long time before mPGES-1 was dis
-
Fig A shows a schematic
2024-09-13
Fig. 2A shows a schematic representation of histological results according to the Franklin and Paxinos Mouse Brain Atlas (2001). The black circles represent the sites of drug infusion that were on-target within the amygdala. Gray circles represent the animals that had infusion locations outside the
15329 records 95/1022 page Previous Next First page 上5页 9192939495 下5页 Last page